 Costal cartilage - Wikipedia
Costal cartilage - WikipediaCoastal cartilage Coastal cartilage Position of the coast cartilages (show in red). and . Preview. DetailsIdentifierscartilagines costalescosto condrio[] This article includes a related reading or , but its sources remain unambiguous because it lacks . Please help this article by more precise appointments. (November 2020) () but its sources remain unclear because it lacks The expensive cartilages are bars that serve to prolong the progress and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the . The costal cartilage is found only at the previous ends of the ribs, providing medial extension. costly cartridges ContentDifferences of ribs 1-12[ ] The first seven pairs are connected to the ; the following three are articulated each with the lower border of the cartilage of the previous rib; the latter two have pointed out extremities, which end on the wall of the . Like ribs, expensive cartilages vary in their , , and direction. The length of the first to seventh increases, then gradually decrease to the twelfth. Its breadth, as well as that of the intervals between them, decreases from the first to the last. They are wide in their attachments to the ribs, and belts towards their patern extremities, except the first two, which are of the same breadth in everything, and the sixth, seventh and eighth, which extend where their margins are in contact. They also vary in direction: the first drops a bit to the stern, the second is horizontal, the third rises slightly, while the others are angular, following the course of the ribs for a short distance, and then ascending to the stern or the previous cartilage. Structure[] Each expensive cartilage has two surfaces, two borders and two limbs. Surfaces[]The previous surface is convex, and looks forward and upward: the one of the first gives attachment to the and to the ; those of the first six or seven at their sternal ends, to the . The others are covered by some of the flat muscles in the abdomen, and give partial attachment to them. The rear surface is concave, and directed backwards and downwards; that of the first one attaches to the , those of the third to the sixth inclusive to the , and the six or seven below the and the . Borders[]From the two frontiers the superior is concave, the lower convex; they adhere to the : the upper border of the sixth also attaches to the . The lower borders of the sixth, seventh, eighth and ninth cartilages present heel projections at the highest points of convexity. These projections carry smooth oblong facets that articulate with facets on small projections from the upper borders of the seventh, eighth, ninth and tenth cartilages, respectively. intercondural joints[] The intercondural joints are formed between the one of . The contiguous frontiers of the sixth, seventh and eighth, and sometimes those of the ninth and tenth, are articulated among themselves by small soft and oblong facets. Each joint is enclosed in a thin, fiber-lined (intercondral ligaments) that pass from a cartilage to another. Sometimes the fifth rib cartilage, more rarely the ninth and the tenth, articulated by its adjacent cartilages by small oval facets; more often the connection is by some ligamentous fibers. intercondral ligaments intercondralExtremities[ ] The side end of each cartilage is continuous with the beary tissue of the rib to which it belongs. The middle end of the first is continuous with the sternon; the middle ends of the six successors are rounded and received in shallow concavities on the side margins of the sternon. The middle ends of the eighth, ninth and tenth cartilages are pointed out, and each one connects with the cartilage immediately above. The 11th and 12th are marked and free. Clinical Significance[]In , expensive cartilages are prone to surface .[] In and , the inflammation of the expensive cartilage occurs. This is a common cause of . It can lead to expensive cartilage. Such injuries often go unnoticed during , but can be diagnosed with . It is usually used to fix the expensive cartilage again on the rib or stern. The costal cartilage can be for reparative use elsewhere in the body. While this is usually done using a , IV can also be used. The procedure presents a lower risk of . Additional images[] Position of expensive cartilages (red). Animation. Previous surface and expensive cartridges. See also[]References[ ]This article incorporates text in the 20th edition of (1918) ab2409480abc107abc41 External links[] Wikimedia Commons has media related to . ########################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################## From of From From From From of Navigation menu Personal tools Named spaces Variants Views More Search Navigation Contributed Tools Printing/exporting Other projects Languages
Accessibility links Search results Osification of the rib element of the seventh cervical vertebrae...Cervical vertebrae - WikipediaCartilage Costal Silence Radiology Reference Item Radiopaedia.org Rabbi Costal Cartilage Reconstruction model surgical Links Foot links
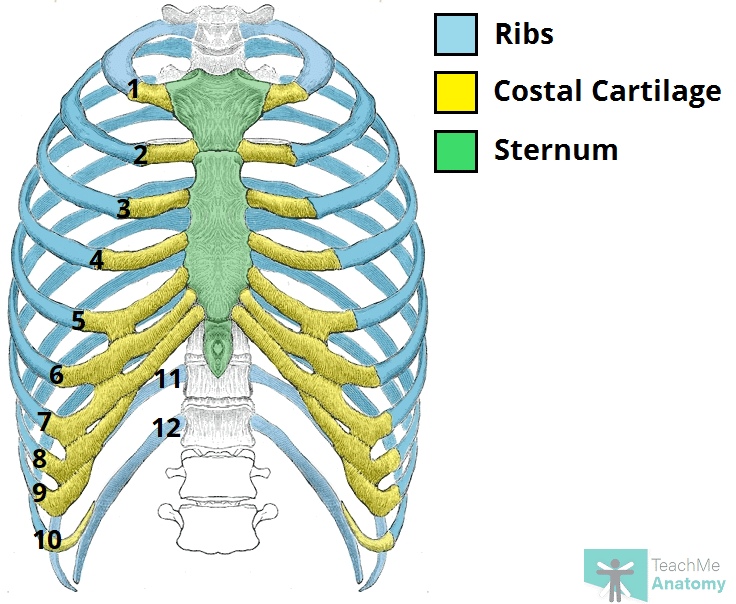
The Ribs - Rib Cage - Articulations - Fracture - TeachMeAnatomy
Rib Cartilage Injury - Masnad Health Clinic
Costal cartilage - Wikipedia
The costal cartilage | Anatomy and functions of the costal cartilage - Anatomy-Medicine.COM:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13220/AU74J0btvJiGYvGGEvSYg_Costochondral_joints__2_.png)
Costochondral joint (junction): Anatomy, function | Kenhub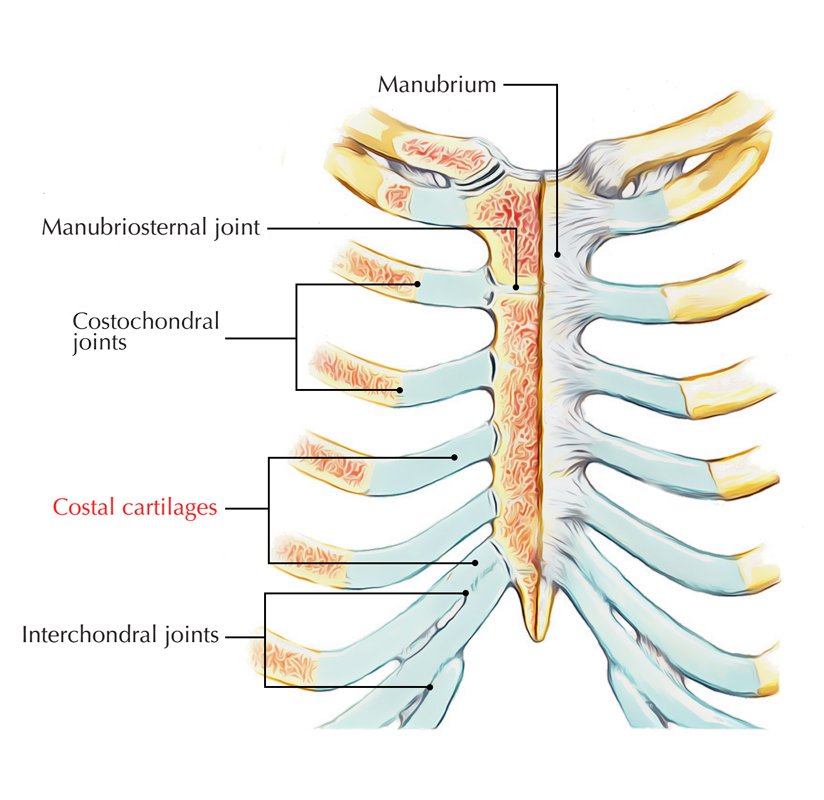
Costal Cartilages – Earth's Lab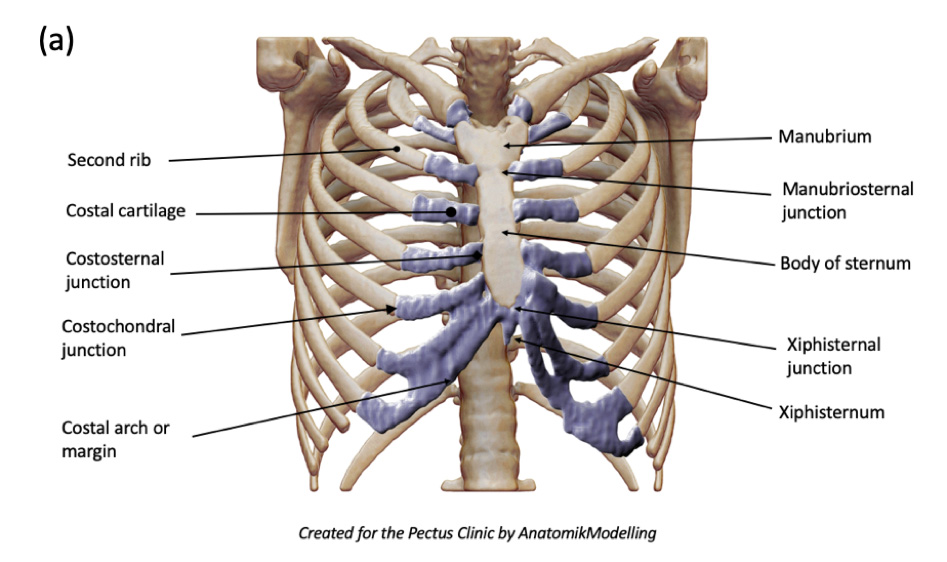
Complex Chest Wall Injury | Rib Injury Clinic
Structure of the Ribcage and Ribs
Pin on Anatomy body parts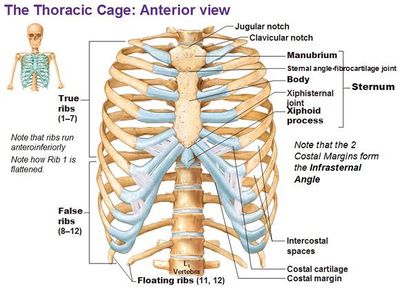
Slipping Rib Syndrome - Physiopedia
Simultaneous Surgical Treatment of Sternum and Costal Cartilage Fractures - The Annals of Thoracic Surgery
Costal Cartilage Anatomy, Function & Diagram | Body Maps | Body map, Function diagram, Anatomy
The thoracic cage – the ribs and sternum | Human Anatomy and Physiology Lab (BSB 141)
Operative findings. (a) Lowermost costal cartilage resection is... | Download Scientific Diagram
Costal Cartilage - Assignment Point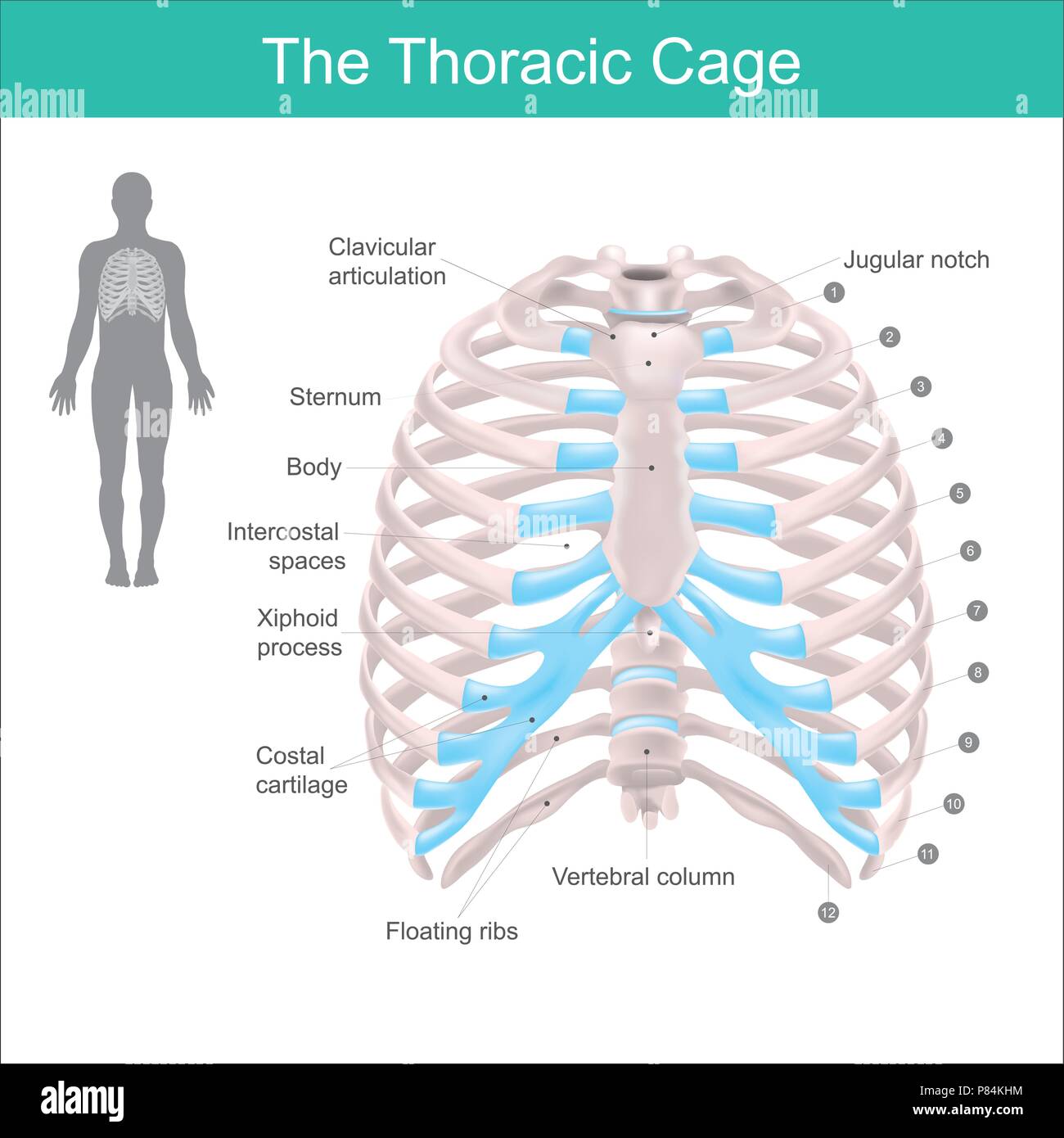
Thoracic cage is made up of bones and cartilage along, It consists of the 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages and the sternum. Illustration Stock Vector Image & Art - Alamy
File:Costal Cartilage.png - Wikimedia Commons
Costal cartilage | anatomy | Britannica
Slipping rib syndrome: an obscure cause of thoracic pain?
File:Third costal cartilage frontal2.png - Wikimedia Commons
Costal Cartilage Rib Rhinoplasty | Dr. Shah
File:Fifth costal cartilage frontal.png - Wikimedia Commons
Rib Cage Sternum Anatomy Costal Cartilage - Unlabeled Rib Cage Diagram, HD Png Download , Transparent Png Image - PNGitem
Ribs: Anatomy, Types, Ossification & Clinical Significance » How To Relief
Understanding Kevin Durant's Rib Cartilage Fracture - In Street Clothes
Cough-induced costal cartilage fracture - ScienceDirect
The costal cartilage stock illustration. Illustration of accurate - 155226764
File:Fisrt costal cartilage animation.gif - Wikimedia Commons
The etiology of pectus carinatum involves overgrowth of costal cartilage and undergrowth of ribs | Braceworks Custom Orthotics
Costal cartilage - Wikidata
Understanding the Mechanical Behavior of Costal Cartilage at Their Curved Exterior Surface Via a Tactile Sensor with a Built-In Probe for Distributed-Deflection Detection | Semantic Scholar
Costal cartilage fracture | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org
Costal Cartilage - Hospital Innovations
Costal Cartilage High Resolution Stock Photography and Images - Alamy
Anatomy Stock Images | torso-ribcage-ribs-costae-costal-cartilage -floating-rib-sternum-front-skin
Costal Cartilage High Res Stock Images | Shutterstock
Sternum w/costal cartilage & ribs - YouTube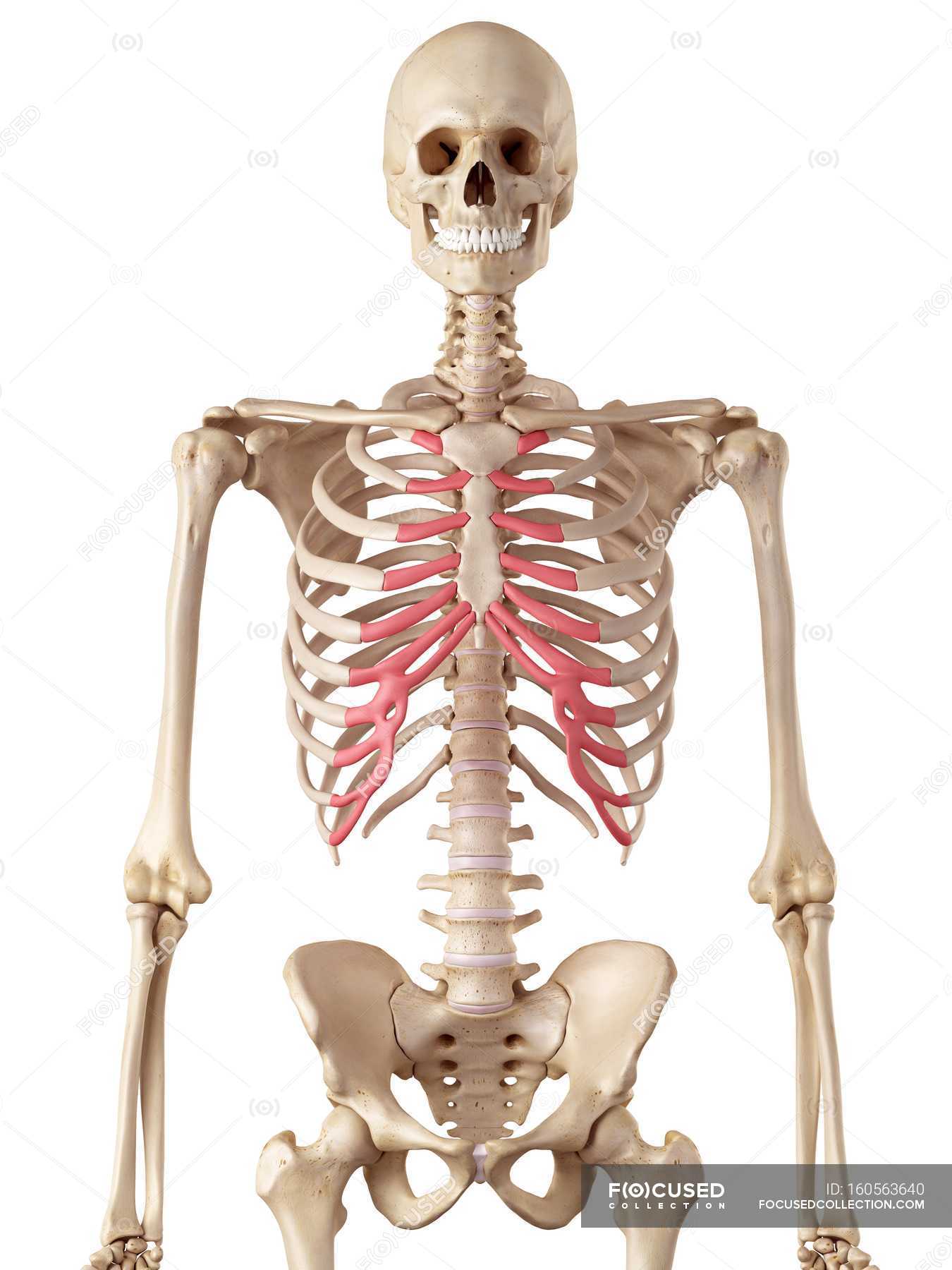
Human rib costal cartilage — 3d, conceptual - Stock Photo | #160563640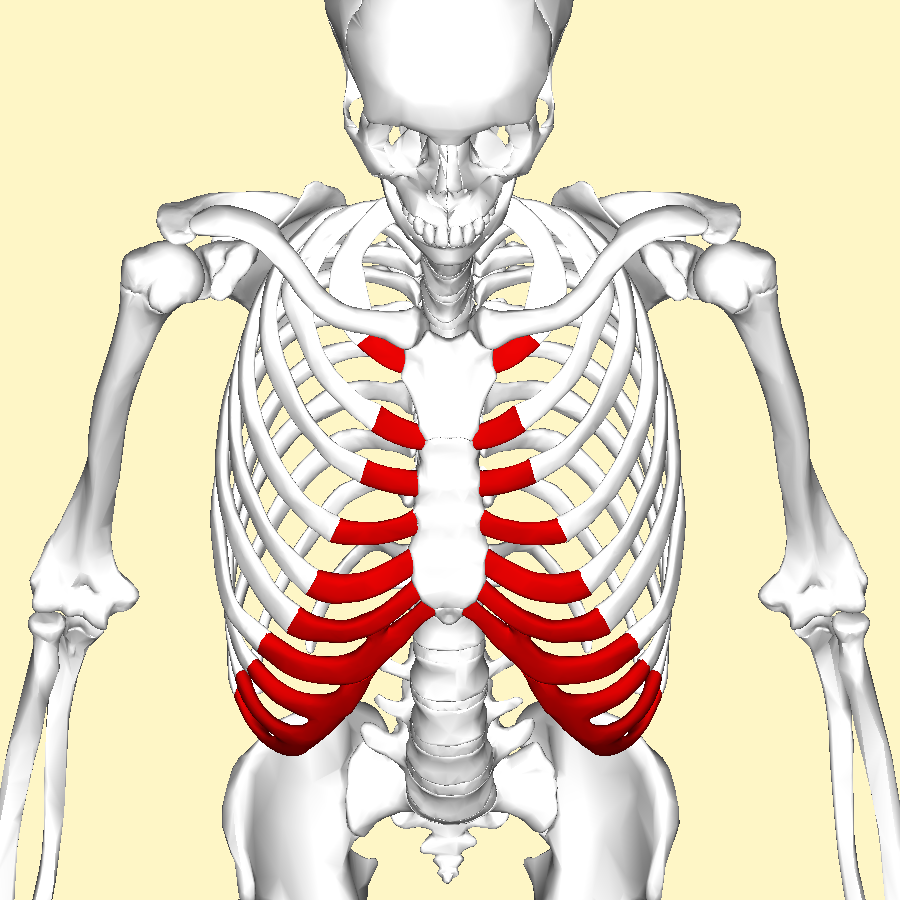
File:Costal cartilages above.png - Wikimedia Commons
Sternum and costal cartilage, anterior view with labels - … | Flickr
 Costal cartilage - Wikipedia
Costal cartilage - Wikipedia



:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13220/AU74J0btvJiGYvGGEvSYg_Costochondral_joints__2_.png)
































Posting Komentar untuk "what is costal cartilage"